
WordPress has a ton of fantastic features. Here we have picked our top 12 useful WordPress features especially helpful for digital marketers.
1. User Privileges
WordPress offers six different types of roles, with varying levels of access. This feature not just makes the assignment of work a lot easier but also provides better security. With this feature, you can prevent people from accessing segments of the website that you, as a website owner, do not want them to.
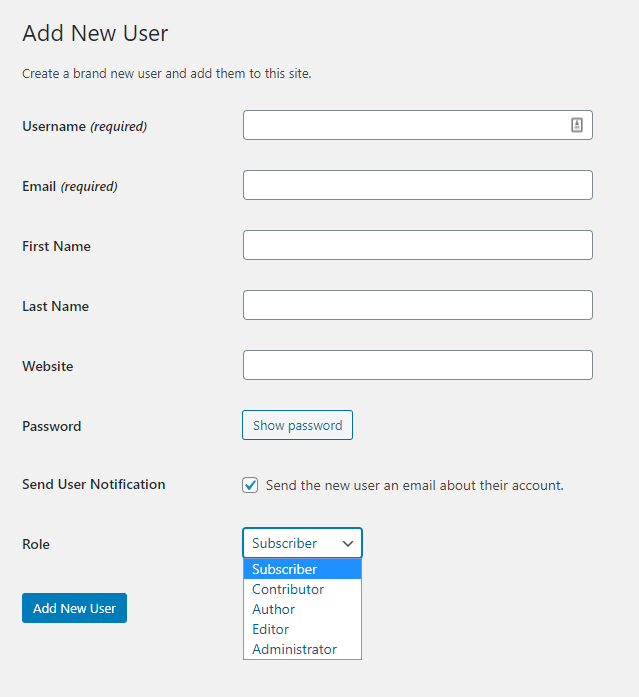
Here is a quick summary of the various roles:
Administrator
This is ideally the business owner or the topmost person in the hierarchy. If you have created the website, you become the administrator by default. An administrator can do absolutely everything from managing content, plugins, and design. The administrator can also assign, change, and delete other roles.
Editor
The editors are the ones who manage content on the website. It can be considered second in line in the hierarchy as they can override actions carried out by authors and contributors. Editors can create, publish, and delete content anywhere on the site. In most businesses, this role is assigned to the marketing head or a content team head.
Author
Authors are one step below editors and, in most business cases, report to someone who has an editor role. They can also create, edit, and delete content; however, these actions can be carried out only on posts assigned to them.
Contributor
Contributors are somewhat similar to authors and can be confused with them. They can also create, edit, and delete their posts like authors. However, the big difference is that they cannot publish content. This role is ideal for interns or new joiners who are yet to learn the ropes.
Subscriber
Subscribers probably have the least access among all the roles. All they can do is access content and have a subscriber profile. This role is not commonly used and is ideal only if you have certain sections are your website that is subscriber exclusive.
Super Admin
Another role that is not as frequently used as it is not relevant for most websites. The super admin, as the name suggests, is one step above admins. This role is required if your business handles multiple WordPress sites or multisite installation. Here the super admin will be responsible for the entire network of sites.
2. Pages, Post and Custom Posts
Before we get into the features pages and posts offer, let’s get into the differences between pages, posts, and also custom posts.
Page
A ‘Page’ in WordPress is used for adding static content generally. For example, Home, Contact Us, About Us, and similar pages.
The page layout comes from the WordPress backend through a ‘page template’ coded in PHP. So when you create a new page, there is an option to pick a page template from the options in the panel on the right side.
You can choose to create a page with header and footer, a page with header and no footer, a full-width page, a boxed page, all depending on the types of page templates available.
You can also have a page template explicitly created for a set of pages that need to be generated periodically. For example, a business can have a page template called Services designed, which can be repurposed every time a new service is to be added.
Post
A ‘Post’ in WordPress is essentially the blog. All posts added to WordPress will follow the same template. Posts can be organized into categories and tags, which we will talk about later in the guide. Posts are used to add recurring content like your blog, news, and updates.
Custom Posts
A third and a compelling option available within WordPress is the Custom Post Type. It is essentially an option in WordPress to create a custom ‘Post’ to represent different and unique content types on the website. Case studies, books, guides, reports are good examples of when a custom post can be created. A custom post is similar to a blog post, but with an option to have its own layout and custom attributes, one can create a custom post for a book with characteristics like ISBN, Genre, Publisher, and design a unique layout. When you log in to the dashboard, you will see a separate menu item called Books, just like Posts. You can add a new ‘Book” like a blog post, use a different set of categories and tags to organize all the books or case studies or reports you plan to upload to the site. And each of these custom posts, since they are different entities, can all have unique layouts from each other.
If you were to upload a case study using the default ‘Posts’ feature, then you use up one level of category just to categorize them as a case study. Similarly, this can be done for books and reports. You are also restricted to one layout for all and with no easy option to add specific attributes to them.
The attributes that you can add to each custom post lets you later access them from the database through a query to fetch, filter, and sort content intelligently. This wouldn’t be possible if all this meta-information were just added into ‘description’ or the ‘main content area’ of the post.
For example, if you have a custom post called Events with custom fields like Venue, Date, Time. Along with the general category and tags, it gives you a multitude of options to organize the Events section. You could fetch all Events happening at a particular venue or location only.
3. Page and Post Privacy Features
WordPress gives you the freedom to choose a visibility setting for every page and even post. Here are the four visibility options
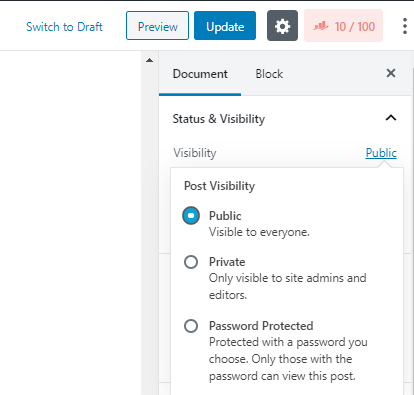
Draft
The draft option, as the name suggests, is for work-in-progress pages and posts. It will not be visible to the outside world.
Private
You can choose this setting when you are done with the draft, and you want it reviewed internally.
Private with password
This is similar to the previous setting, except here you can add a password. This feature is useful when you want to restrict access to only some visitors or some internal stakeholders.
Published
The default setting in WordPress for both posts and pages is Public or in other words published. Public visibility essentially means that the content will be visible to everyone.
4. Image Editing
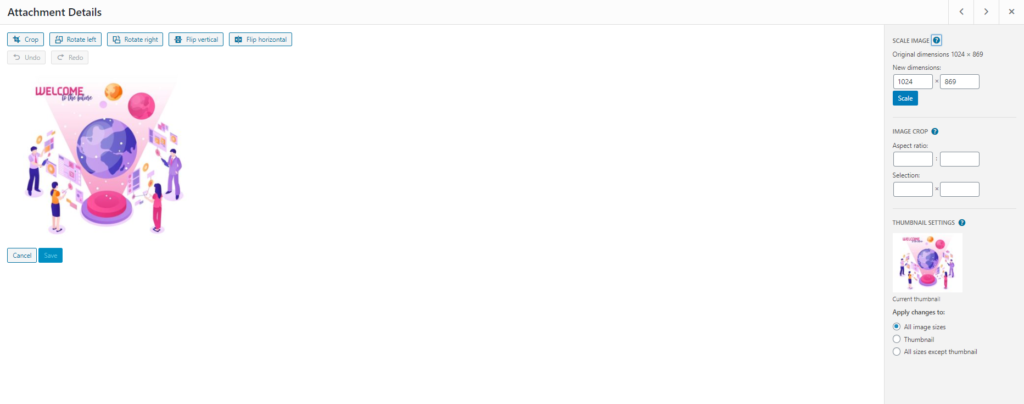
Once you have uploaded an image to the media library on WordPress, there are a few features that allow some basic editing. This includes resizing, cropping, rotating, and even reverting edits. Though these may seem like a few basic editing options, often, they are more than enough to manage your images.
5. Page and Post Revisions
Sometimes when working on a post or page, you might accidentally save some changes and want to revert to the previous version. This can be done easily with the page and post revisions. WordPress makes this possible by automatically saving temporary alterations.
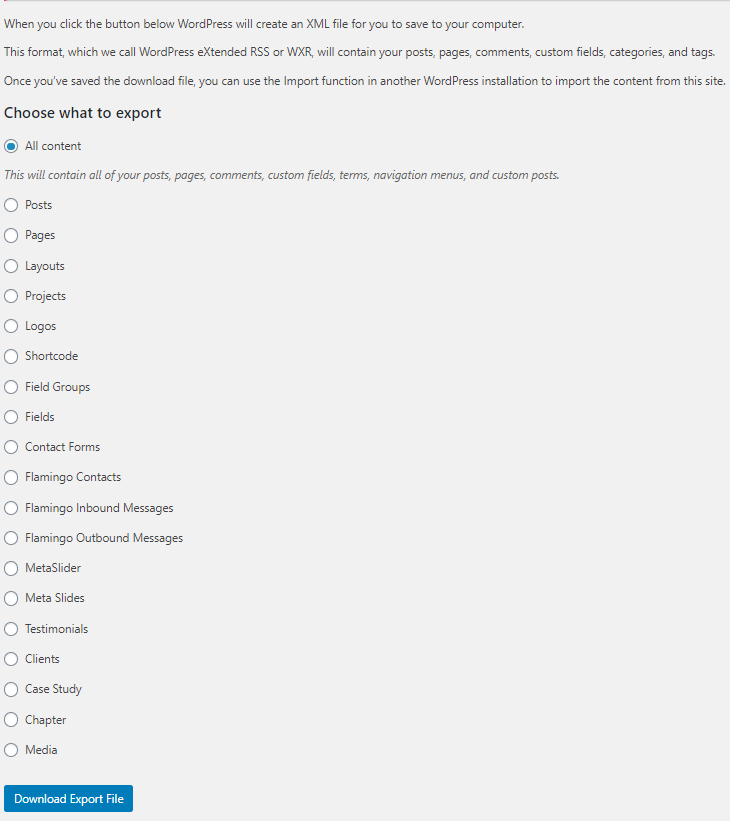
6. Importing & Exporting Blog Content
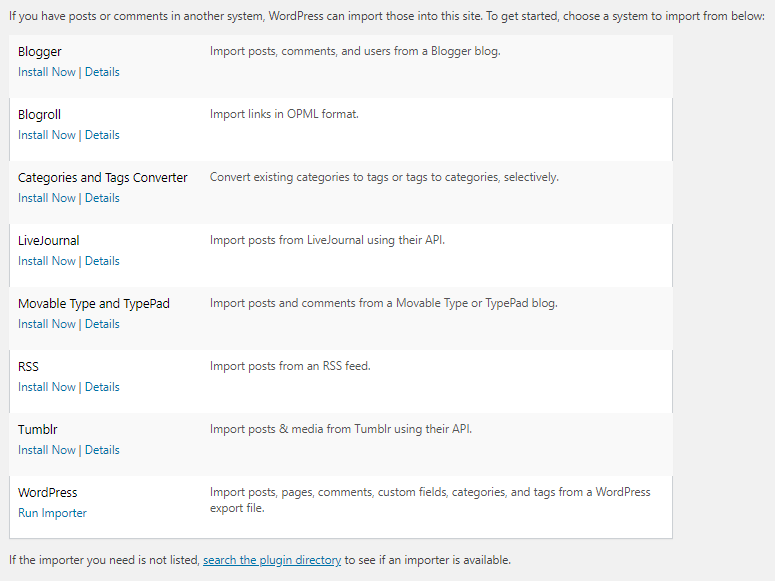
WordPress allows you to import content into your site from an extensive list of different publishing systems. Additionally, if you want to export content from an option not listed, you can do so by installing a plugin. Exporting content is also as simple. You can export everything from posts, pages to even menus. These tools make moving to and from a different publishing system or website simpler.
7. Permalinks
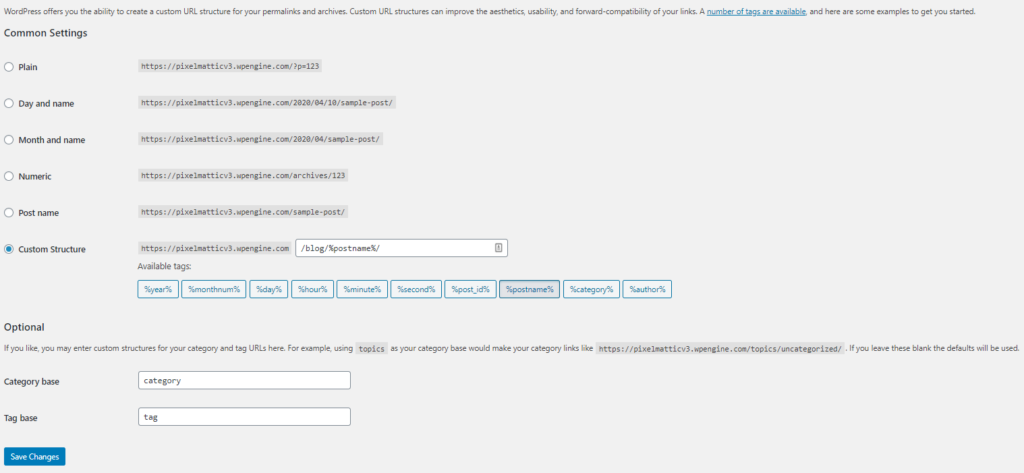
Permalinks, as the name suggests, is a permanent link to every page on your website. WordPress offers you the additional feature of customizing URL structure. This feature helps with the usability and forward compatibility of the links. Moreover, permalinks bring an SEO benefit as it allows URLs to be descriptive and human-readable.
8. Editor
WordPress rolled out the block editor, also known as Gutenberg, in 2018. If you have been using the classic editor and not ready to make a move yet, don’t worry! You still have the option of switching back to the classic editor. Moreover, WordPress is expected to continue to support the classic editor at least until 2022.
Note – These are not features that you can add to your website using plugins. We will cover them in the following sections, particularly those relevant to your marketing needs.
9. Content Structure
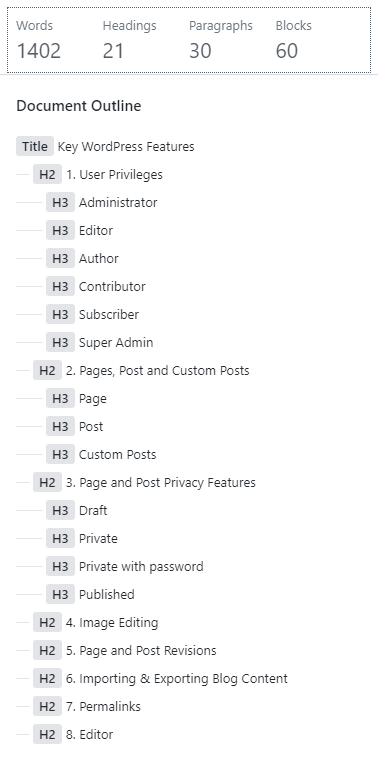
The new Block Editor in WordPress brings with it some new features to WordPress. If you click on the “i” icon at the top left of the editor, you will popup similar to the screenshot above. It gives you a breakup of some important elements of your blog post content.
Knowing if you’ve used H1, H2 and H3 tags appropriately to format and style your content is helpful from a readability and SEO point of view.
A quick look at the word count is good feedback to have when you’re writing content.
10. Dashboard Screen Widget Options
If you want to quickly customize your WordPress Dashboard view when you login, you can use the ‘Screen Option’ tab visible on the Dashboard page.
You can enable and disable the widgets from this options panel. These widgets can also be moved and reorganized as per your liking.
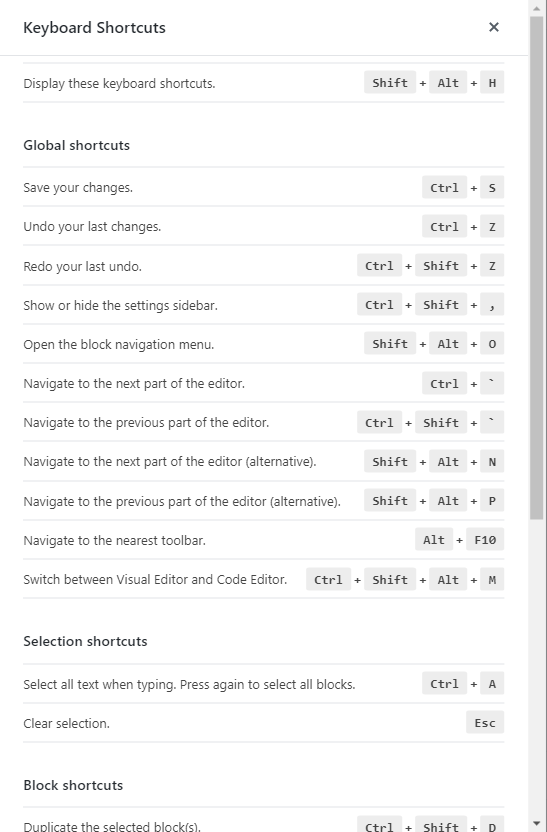
11. Keyboard Shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts are a big time saver. And if you love using shortcuts in other tools, then learn some of the ones below to speed up your editing process.
12. Embed Multimedia
It’s as simple as copying and pasting the Youtube link in the editor and you will see the preview added automatically.

A full list of supported sites for this feature is available here.